预备知识
RefSeq数据资源与Ensembl数据资源- 什么是
PDB - 什么是
UniProt-KB - 什么是可变剪切(Alternative Splicing)
- 什么是蛋白质一级结构 (序列)
- 什么是蛋白质三级结构 (晶体结构)
从中心法则谈起: 基因位点到蛋白质位点
 |
| 1. from genomic location to transcript site |
| 2. from transcript site to protein site |
| 3. from protein site to crystal site |
在自然生物体内,一生物功能的实现,往往需要具有生物学效应的蛋白质参与实施。而这蛋白从何而来? 经过多肽链空间折叠而来。多肽链从何而来? 由信使RNA(message RNA, mRNA)经过核糖体翻译而来。那么mRNA又从何而来,经过一基因的转录,转录后修饰,进行可变剪切等而来。这样来看,从三核苷酸密码子到多肽链的氨基酸再到蛋白质结构中的氨基酸残基(Residue),在逻辑上也就存在对应关系。这个对应关系建立在核酸序列的顺序性以及衍生的多肽链序列的顺序性的基础上。
从基因组位置映射到转录本位点以及从转录本位点映射至蛋白质位点的工作,面临着两大问题:
- 基因组数据资源的庞大,映射位点工作尽管逻辑与计算上简单但是需要大量计算资源
- 基因组数据标识、转录本数据标识、蛋白质数据标识都会随着国际科学研究的进展而进行更新,在ID标识符与具体的位点上常常有比较大的更新
幸运的是,上述层面的工作被诸如NCBI(美国国家生物技术信息中心)以及EBI(欧洲生物信息学中心)等机构承包。他们本身是数据资源的存储、更新方,同时具有充足的计算资源与经费,能够便捷且良好地完成这些工作。在获取人类基因组突变相关数据时,基本上在得到所关注的基因组层面的突变位置时,数据提供方也会给出映射至转录本或蛋白质可变剪切体层面的位点(标识符常采用Ensembl Gene/Transcript/Protein或RefSeq Nucleotide/Transcript/Protein)。
注: 若原始突变数据没有给出具体的蛋白质位点,也有大量工具可以进行转化,本处不再赘述
而在研究蛋白质时,基本上离不开UniProt-KB这一数据资源,其对大量物种的每个基因得到的蛋白质都赋予特定标识符(i.e. UniProt Accession/Entry: P21359),同时有专门人员对大量条目进行专家鉴定(被鉴定过的UniProt条目会被标记上reviewed,反之unreviewed);没被review过的条目一般是计算方法根据同源性等理论预测出的条目,一般不采用。值得注意的是,UniProt-KB考虑到了转录本层面的可变剪切现象 (click here to learn more),因而在具有可变剪切现象的UniProt条目下,其也给出了不同的可变剪切条目,称为isoform (e.g P21359-1, P21359-2, P21359-3, P21359-4, P21359-5)。这些可变剪切体在序列上有所差异,因而对应的完整蛋白质结构可能有所不同。(若某部分可变剪切体的序列与其他部分可变剪切体的序列差异达到一定程度,UniProt-KB将创建新的条目来给那一部分的isoform)。在这些isoform中,UniProt-KB会选出一isofrom作为canonical sequence来代表该UniProt条目(一般是选最长的,但也不一定)。选定的canonical isoform在UniProt-KB中一般不会显示其具体的isoform编号(例如P21359的canonical isoform为P21359-1,那在UniProt-KB中说P21359一般就是指P21359-1)。
注: UniProt-KB会用诸如VAR_032459等来表示各个可变剪切体(isoform)的sequence与canonical sequence的差异
作为UniProt-KB以及Ensembl的持有方,EBI将ensembl与UniProt条目进行了匹配,且对于reviewed UniProt条目精确到了具体的对应isoform;同时与NCBI合作,将RefSeq资源也进行了如上对应。样例:
Ensembl:
1
2
3
4
ENST00000356175; ENSP00000348498; ENSG00000196712 [P21359-2]
ENST00000358273; ENSP00000351015; ENSG00000196712 [P21359-1]
ENST00000431387; ENSP00000412921; ENSG00000196712 [P21359-5]
ENST00000487476; ENSP00000491589; ENSG00000196712 [P21359-3]
RefSeq:
1
2
3
NP_000258.1, NM_000267.3 [P21359-2]
NP_001035957.1, NM_001042492.2 [P21359-1]
NP_001121619.1, NM_001128147.2 [P21359-5]
注: 不是所有的UniProt条目对应的原始转录本都有发生可变剪切现象
目前为止是从基因组位点到蛋白质位点(UniProt Isoform层面)的工作。
Code to Achieve Your Goal 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
from pdb_profiling import default_config
from pdb_profiling.processors import Identifier
default_config(your_output_folder)
demo = Identifier('ENST00000431387')
entry, isoform = demo.map2unp().result()
print(f"UniProt Entry: {entry}, UniProt Isoform: {isoform}")
# UniProt Entry: P21359, UniProt Isoform: P21359-5
从UniProt到PDB结构: 为什么有些事情不是那么顺理成章
从基因序列到转录本序列再到对应的可变剪切体氨基酸序列,都是站在所研究的基因的视角上,要求着各个层面上序列对应关系的一致性(尤其是转录本发生可变剪切后翻译出的蛋白质序列要与对应的UniProt isoform完全一致,i.e ENSP00000351015的序列和P21359-1的序列完全一致才匹配上),这样才能实现位点的精确对应,不会出现错配的情况。而UniProt与PDB之间可以通过氨基酸序列匹配、物种匹配等便捷建立匹配关系。但对于PDB晶体结构,有如下情况需要澄清:
- 通常,现有的序列匹配结果资源是将UniProt Isofrom的序列与PDB链的SEQRES完整序列(不论有无确切解析出的空间坐标、无论是否是人工添加的序列片段等)进行匹配;为什么要说这个? 请看下面的内容
- 解析出该结构的晶体学科学家不一定就是按照其研究的基因或蛋白的原始序列进行结晶,其可能是编辑过一级序列进行C端添加人工序列、对某段序列进行了重复、减去了某段序列、插入某段序列等增删改操作;
- 晶体学家解析结构的方法有X-ray(X射线)、NMR(核磁共振)、EM(电镜)等方法,不同方法得到的同一目标蛋白结构在精度上有所不同,且存在部分预期要结晶的氨基酸序列却没结晶出来(所以结构中间可能会中断一部分, missing residues)或是只结晶出了氨基酸残基的主链原子没得到侧链原子信息
- 某一氨基酸残基侧链原子完全丢失或丢失到无法确定氨基酸种类且未知确切的一级结构就无法确定该氨基酸为何种氨基酸,氨基酸残基用
UNK表示,单字符用X表示 - 若某一氨基酸残基的侧链原子部分缺失或完全丢失,但知道一级结构就仍能确定该氨基酸种类
- 某一氨基酸残基侧链原子完全丢失或丢失到无法确定氨基酸种类且未知确切的一级结构就无法确定该氨基酸为何种氨基酸,氨基酸残基用
- 同时,结晶出的结构的某些残基可能会发生糖基化、酰基化、磷酸化等修饰,使得氨基酸残基侧链改变,相当于氨基酸种类变化,这就与原一级结构对应的氨基酸有了差异
- 一级结构决定三级结构,一级结构的些许差异对于三级结构的空间构象可能有着不小的影响
- 有的晶体结构在涵盖了匹配上的蛋白序列(UniProt Isoform sequence)之外,还有其他序列片段被结晶了出来,这些”额外”的片段在空间结构上可能对匹配上的片段部分产生构象等层面的影响
- 一条匹配上的PDB链不一定就完全覆盖了目标蛋白的全部序列,可能只是其中的某一小部分;匹配上的不同PDB链对该UniProt Isoform的覆盖范围可能存在差异
- 此外,晶体学家在自己提交的PDB文件中,对与氨基酸残基的编号(即
author_residue_number)可能参考的是当时的匹配上的UniProt Isoform或是其他参考序列的编号或是完全自己编号;单单从UniProt Isoform上的位点编号并不能直接就将认定为PDB链上的编号;且作者除了使用数字编号还可能会添加author_insertion_code这样的字母符号来标注一些Insertion效应的氨基酸残基(e.g 3sqh A链的author_residue_number 60号位),这就使得单独只用author_residue_number并不能唯一指定该PDB链中的氨基酸残基
上述这些要求着我们对UniProt Isoform与PDB链的序列匹配的identity进行把控,同时考虑到missing residues等的影响,选择出与目标UniProt Isoform最匹配的PDB链;同时,考虑到不同PDB链的不同覆盖范围,尽量选择覆盖范围最大的链,并可选择多条链使得这些链尽可能覆盖完整蛋白质,以此来尽多地囊括我们所要研究的位点;此外还需注意位点编号层面的对应。
About Mapped Range: From EBI’s SIFTS
我们下面来界定如下概念,以此来明确PDB文件中位点对应关系
pdb_start&pdb_end: PDB链序列中对齐匹配(alignment)的起始位置和结束位置unp_start&unp_end: UniProt Isoform序列中对齐匹配(alignment)的起始位置和结束位置
注意,上述起始/结束位置都是从1开始计数的位点索引;对于PDB链序列即为该链的SEQRES完整序列的位置索引(即residue_number),与author_residue_number无关。
Click to view Raw JSON data:
```json { "1a01": { "UniProt": { "P68871": { "identifier": "HBB_HUMAN", "name": "HBB_HUMAN", "mappings": [{ "entity_id": 2, "end": { "author_residue_number": 146, "author_insertion_code": "", "residue_number": 146 }, "chain_id": "B", "pdb_start": 1, "start": { "author_residue_number": 1, "author_insertion_code": "", "residue_number": 1 }, "unp_end": 147, "pdb_end": 146, "struct_asym_id": "B", "unp_start": 2, "is_canonical": true, "identity": 0.99 }, { "entity_id": 2, "end": { "author_residue_number": 146, "author_insertion_code": "", "residue_number": 146 }, "chain_id": "D", "pdb_start": 1, "start": { "author_residue_number": 1, "author_insertion_code": "", "residue_number": 1 }, "unp_end": 147, "pdb_end": 146, "struct_asym_id": "D", "unp_start": 2, "is_canonical": true, "identity": 0.99 }] }, "P69905": { "identifier": "HBA_HUMAN", "name": "HBA_HUMAN", "mappings": [{ "entity_id": 1, "end": { "author_residue_number": 141, "author_insertion_code": "", "residue_number": 141 }, "chain_id": "A", "pdb_start": 1, "start": { "author_residue_number": 1, "author_insertion_code": "", "residue_number": 1 }, "unp_end": 142, "pdb_end": 141, "struct_asym_id": "A", "unp_start": 2, "is_canonical": true, "identity": 1 }, { "entity_id": 1, "end": { "author_residue_number": 141, "author_insertion_code": "", "residue_number": 141 }, "chain_id": "C", "pdb_start": 1, "start": { "author_residue_number": 1, "author_insertion_code": "", "residue_number": 1 }, "unp_end": 142, "pdb_end": 141, "struct_asym_id": "C", "unp_start": 2, "is_canonical": true, "identity": 1 }] } } } } ```Click to view Converted Tabular Format:
| UniProt | chain_id | end | entity_id | identifier | identity | is_canonical | name | pdb_end | pdb_id | pdb_start | start | struct_asym_id | unp_end | unp_start |
| P68871 | B | {"author_residue_number":146,"author_insertion_code":"","residue_number":146} | 2 | HBB_HUMAN | 0.99 | TRUE | HBB_HUMAN | 146 | 1a01 | 1 | {"author_residue_number":1,"author_insertion_code":"","residue_number":1} | B | 147 | 2 |
| P68871 | D | {"author_residue_number":146,"author_insertion_code":"","residue_number":146} | 2 | HBB_HUMAN | 0.99 | TRUE | HBB_HUMAN | 146 | 1a01 | 1 | {"author_residue_number":1,"author_insertion_code":"","residue_number":1} | D | 147 | 2 |
| P69905 | A | {"author_residue_number":141,"author_insertion_code":"","residue_number":141} | 1 | HBA_HUMAN | 1 | TRUE | HBA_HUMAN | 141 | 1a01 | 1 | {"author_residue_number":1,"author_insertion_code":"","residue_number":1} | A | 142 | 2 |
| P69905 | C | {"author_residue_number":141,"author_insertion_code":"","residue_number":141} | 1 | HBA_HUMAN | 1 | TRUE | HBA_HUMAN | 141 | 1a01 | 1 | {"author_residue_number":1,"author_insertion_code":"","residue_number":1} | C | 142 | 2 |
 |
| P68871 mapped with 1a01 Chain B |
About Mapped Range: Reformated by pdb-profiling
pdb_range: 将同一对UniProt Isoform与PDB链的匹配范围整体成区间格式(convert pdb_start&pdb_end to intervel/range format)unp_range: 将同一对UniProt Isoform与PDB链的匹配范围整体成区间格式(convert unp_start&unp_end to intervel/range format)
| UniProt | is_canonical | pdb_id | entity_id | chain_id | struct_asym_id | identity | pdb_range | unp_range |
| P21359 | True | 1nf1 | 1 | A | A | 0.94 | [[1,333]] | [[1198,1551]] |
| P21359 | True | 3pg7 | 1 | A | A | 1.00 | [[1,256]] | [[1581,1837]] |
| P21359 | True | 6v65 | 2 | B | B | 0.94 | [[2,329]] | [[1203,1551]] |
| P21359 | True | 3peg | 1 | A | A | 0.94 | [[5,172],[174,290]] | [[1566,1733],[1721,1837]] |
| Q13303-3 | False | 1zsx | 1 | A | A | 0.95 | [[26,347]] | [[72,408]] |
| P30038-3 | False | 4oe5 | 1 | D | D | 0.91 | [[4,381],[433,549]] | [[18,395],[396,512]] |
| P00441 | True | 5j0c | 1 | A | A | 0.92 (0.60) | [[90,114],[3,23],[28,68],[72,85]] | [[2,26],[29,49],[84,124],[141,154]] |
About Mapped Range: Detected by pdb-profiling
sifts_range_tagSafeInsertionDeletionInDel
reversed- SIFTS是以PDB Chain Sequence的视角来匹配序列片段,少数情况会有把部分unp序列反向匹配(i.e. P00441 5j0c A)
- “5j0c - it the circular permutant structure where authors have swapped the few chunk protein from front and back -(figure 2 in https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/jacs.6b05151). That’s why you see “the head of the UniProt sequence is mapped with the tail of the PDB-Chain sequence” – from Preeti Choudhary
repeated- (i.e. Q7KZ85-3 6gmh M)
- “In SIFTS, the segment generation is done from PDB point of view, that’s why you will see continuous pdb ranges. Seldom, in protein structures, you may see a same protein (uniprot accession) is present in copies/or is repeated” – from Preeti Choudhary
| UniProt | pdb_id | entity_id | chain_id | identity | new_pdb_range | new_unp_range | sifts_range_tag | reversed | repeated |
| P21359 | 1nf1 | 1 | A | 0.94 | ((1, 174), (175, 333)) | ((1198, 1371), (1393, 1551)) | Deletion | False | False |
| P21359 | 3pg7 | 1 | A | 1.00 | ((1, 191), (192, 256)) | ((1581, 1771), (1773, 1837)) | Deletion | False | False |
| P21359 | 6v65 | 2 | B | 0.94 | ((2, 170), (171, 329)) | ((1203, 1371), (1393, 1551)) | Deletion | False | False |
| P21359 | 3peg | 1 | A | 0.94 | [[5,172],[174,290]] | [[1566,1733],[1721,1837]] | InDel_1 | False | True |
| Q13303-3 | 1zsx | 1 | A | 0.95 | ((26, 154), (155, 347)) | ((72, 200), (216, 408)) | Deletion | False | False |
| P30038-3 | 4oe5 | 1 | D | 0.91 | [[4,381],[433,549]] | [[18,395],[396,512]] | Insertion | False | False |
| P00441 | 5j0c | 1 | A | 0.92 (0.60) | [[90,114],[3,23],[28,68],[72,85]] | [[2,26],[29,49],[84,124],[141,154]] | InDel_1 | True | False |
| Q7KZ85-3 | 6gmh | 13 | M | 1.00 | [[4,619],[1616,1726],[621,624]] | [[1,616],[616,726],[617,620]] | InDel_1 | True | True |
 |
| Insertion: P30038-3 mapped with 4oe5 Chain D |
 |
| Deletion: Q13303-3 mapped with 1zsx Chain A |
 |
| InDel: Q01780 mapped with 6d6q Chain J |
About Mapped Range: Fixed by pdb-profiling
new_pdb_rangenew_unp_range
上面的new_pdb_range,new_unp_range两列是程序在判断出sifts_range_tag,repeated,reversed后重新计算生成的匹配区域。
Code to Achieve Your Goal 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
from pdb_profiling import default_config
from pdb_profiling.processors import SIFTS
default_config(your_output_folder)
'''
NOTE:
程序默认会对PDB链层面、PDB条目层面进行筛选过滤
(可通过print(SIFTS.chain_filter);print(SIFTS.entry_filter)查看过滤条件)
若不想过滤则将下面的代码#去掉
(也可更改过滤条件,过滤语句基于pandas.DataFrame.query)
'''
# SIFTS.chain_filter, SIFTS.entry_filter = '', ''
demo = SIFTS('P21359')
df1 = demo.pipe_select_mo().result()
# NOTE: df1里的所有结果是该UniProt匹配上的所有PDB链
# NOTE: 程序推荐的是select_tag为True的,根据一系列打分排名; 同时考虑了覆盖范围,尽多选择覆盖完该UniProt Isoform序列的结构
df1[df1.select_tag.eq(True)]
程序首先调用EBI的SIFTS资源得到与UniProt Isoform在序列上匹配到的PDB结构(具体到匹配到哪一条链, 序列相似性identity也有给出); 然后是在考虑每条PDB链对该UniProt序列的匹配范围(new_unp_range, new_pdb_range)下,选出质量较高的链(评估质量的因素包括序列匹配好坏,丢失残基比例等)。
这个质量好坏用RAW_BS这一分值表示,越高说明该PDB链与UniProt的匹配理想程度越高;select_rank为按['RAW_BS', '1/resolution', 'revision_date', 'id_score']依次排序(然后选RAW_BS高的,一样就看1/resolution,再一样就看revision_date,最后看id_score)。选中了某条链后,还会看排在后面的链的覆盖范围与已经选中的链的覆盖范围的差异(metric采用overlap coefficient),达到一定阈值(<0.2)就也选定(采用贪婪算法)。因此在结果中,若有多个链的select_tag为true,就是说这些链与该UniProt Isoform匹配度相对较好且覆盖UniProt Isoform的部分有足够差异,因此都选上。
现在我们有了选定的UniProt Isoform与PDB Chain的对应关系及对应匹配范围信息,将UniProt Isoform上的位点对应上PDB Chain上的residue_number或PDB提交者定义的author_residue_number+author_insertion_code就很简单了,具体参见这个链接。
补充一下
从UniProt Isoform映射到PDB链也存在着数据量大、数据源经常更新(增删改)的问题。但这个问题随着EBI发布PDBe RESTful API而顺畅解决,程序调用其提供的API接口即能实时获取最新的映射关系数据。
聊聊三维结构数据: 数据文件的组织形式
Logical Structure
- Entry
- Assembly
- Model
- Entity
- Chain
- Residue
- Residue Conformer
- Atom
- Residue Conformer
- Residue
- Chain
- Entity
- Model
- Assembly
Asymmetric Unit & Biological Assembly/Unit
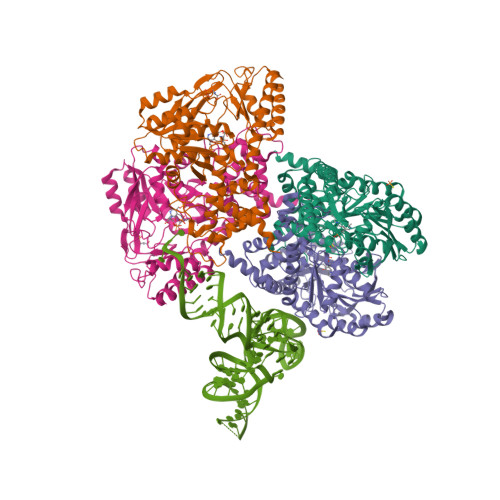
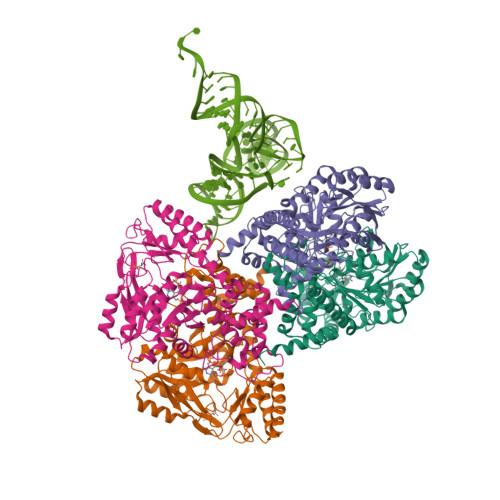
一pdb_id对应的条目(Entry)中可能会有多条链(Chain),这些链中SEQRES序列完全一致的属于同一Entity。晶体学家在解析完晶体结构后,提交的PDB文件数据中所有链(蛋白/核酸/配体/碳水化合物/水)分子构成了该PDB条目的asymmetric unit (assembly_id: 0)。作者在提交上述原本的asymmetric unit文件后,也会考虑到自己所结晶出的蛋白质在生物学效应中的聚体形式,利用先验的生物学知识或是软件(i.e. PISA)依据原asymmetric unit文件生成biological assembly:对asymmetric unit中的链选取子集,有时会对部分链进行复制、旋转、位移等操作,生成新的链,并产生新的链-链相互作用。
| Asymmetric unit of 6v6f | Biological assembly 1 of 6v6f |
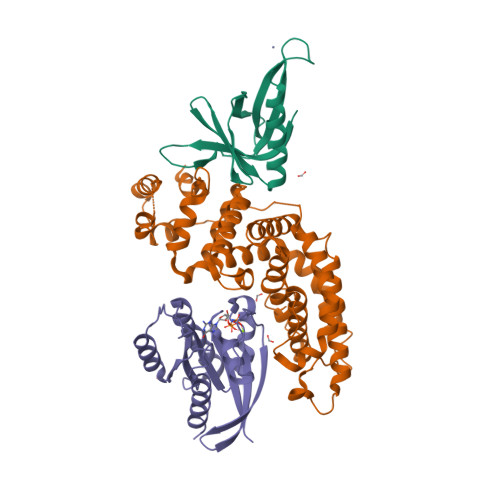 | 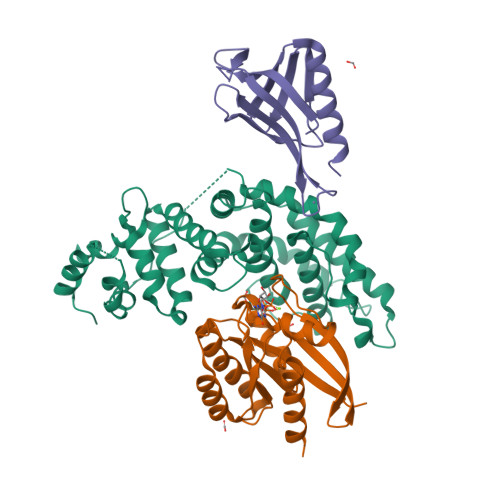 |
| Asymmetric unit of 3hl2 | Biological assembly 1 of 3hl2 | Biological assembly 2 of 3hl2 |
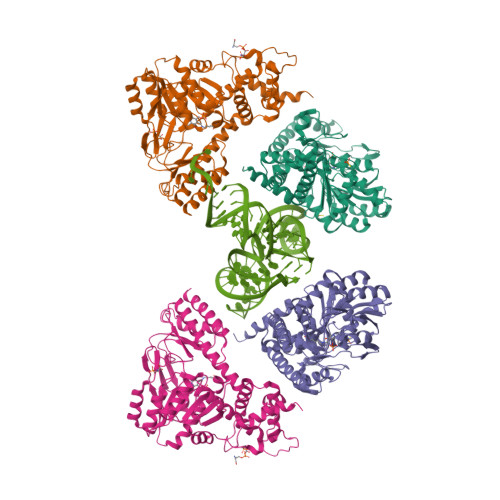 |  |  |
| Asymmetric unit of 2q4n | Biological assembly 1 of 2q4n |
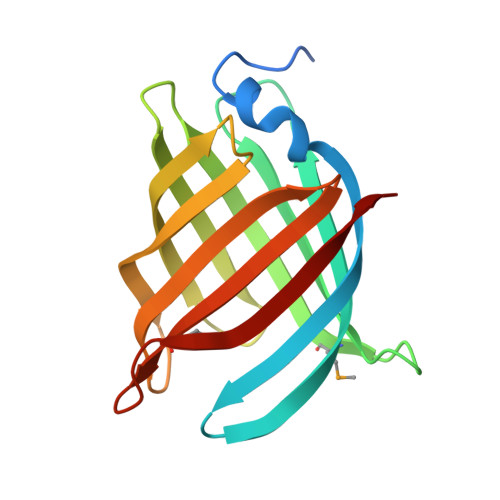 | 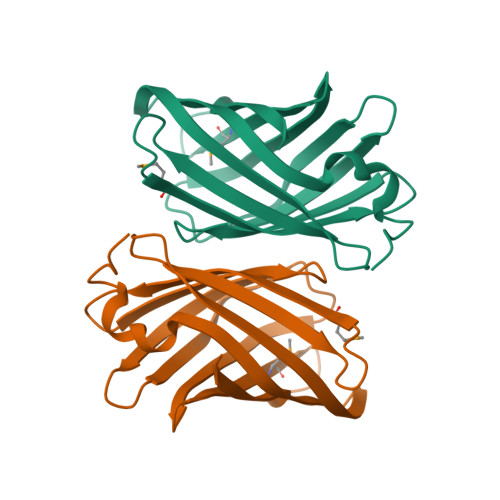 |
Code to Achieve Your Goal 3
pdb-profiling也同时可以输出二元链链相互作用数据。对于蛋白-蛋白相互作用,其同时整合了PISA给出的interacting interface信息以及Interactome3D给出的二元相互作用数据。需要注意到,这些对应数据并不局限于asymmetric unit,不同biological assembly中的相互作用可能存在差异,pdb-profiling都给出。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
df2 = demo.pipe_select_ho(run_as_completed=True, progress_bar=tqdm).result()
# NOTE: df2里的所有结果是该UniProt匹配上的所有同聚体相互作用链;每一行就是一对相互作用 (同属于一个蛋白的两条链相互作用)
# NOTE: 程序推荐的是i_select_tag为True的,根据一系列打分排名; 同时考虑了interface覆盖范围,尽多选择各种类型同聚体相互作用结构
df3 = demo.pipe_select_he(run_as_completed=True, progress_bar=tqdm).result()
# NOTE: df3里的所有结果是该UniProt匹配上的所有异聚体相互作用链;每一行就是一对相互作用 (属于两个不同个蛋白的两条链相互作用);
# NOTE: 程序推荐的是i_select_tag为True的,根据一系列打分排名; 同时考虑了interface覆盖范围,尽多选择同一对异聚体相互作用下的各种相互作用结构
# NOTE: 输入的UniProt Isoform可能是UniProt_1也可能是UniProt_2
# NOTE: 同一对异聚体相互作用可用i_group认定
下面是对结果列名的一些解释:
_1: denoted as the partner chain 1_2: denoted as the partner chain 2assembly_id- 0 stands for asymmetric unit
- 1 stands for biological assembly 1
- 2 stands for biological assembly 2
- and so on
- for what is asymmetric unit & biological assembly? please click the link
model_id: the model ID of the chain in the corresponding biological assembly PDB format file- 0 denoted as the first model
unp_range_DSC: the Dice Similarity Coefficient ofnew_unp_range_1&new_unp_range_2interface_range_1: the range of the interaction’s interface in the aspect of partner1 chain (Index from 1)interface_range_2: the range of the interaction’s interface in the aspect of partner2 chain (Index from 1)unp_interface_range_1: the range of the interaction’s interface in the aspect of partner1 chain (mapped to the UniProt Isoforom)unp_interface_range_2: the range of the interaction’s interface in the aspect of partner2 chain (mapped to the UniProt Isoforom)i_select_tag: whether in the recommanded interaction representative seti_select_rank: the rank among all the interacting-chains (1st denoted as the best)in_i3d: 判断这一PPI是否在Interactome3D数据集中(UniProt Entry相互作用以及对应biological assembly、model的PDB Chain相互作用都在数据集中才为True)i_group: the Heteromeric Interaction Group
| Asymmetric unit of 4l57 | Biological assembly 1 of 4l57 |
路在何方: 站在蛋白质位点的视角,有何应用
Concept
- $\Delta G_{\text{mut}}$
- $\Delta G_{\text{wild}}$
- $\Delta\Delta G$
- Stability
- Binding Affinity
- Disease phenotype predicted by Large-Scle-Study v.s. Molecular phenotype prediction
 |  |
| DDG of Stability for Monomeric protein | DDG of Binding Affinity for Homomeric/Heteromeric protein |
Material
- Mutations
- Protein tertiary structures
Method
FoldXMCSM (stability)MCSM PPIpdb-profiling