Entropy (Measuring Information)
Definition of Shannon’s Entropy
- 信息中有
- 有意义信息(非冗余)
- 无意义信息
- 冗余信息
- Bit作为信息量(Information)的衡量方式
- Bit = 0 or 1 (是或不是, 天然等概率)
- Bit = Uncertainty divided by 2
- 对于Bit计算方法的两种直观理解方式
- N种情况(state) -> log计算 -> 得到信息量 $\log_{2}^{N}$
- 可以这样理解,N种情况等可能(Uncertainty divided by N, N is uncertainty reduction factor),把所有情况赋予二进制编码, 为了完整描述每一情况,需要的二进制位数即是传递该情况所需的信息量
- 在此种理解方式下
- N只能为正整数?
- 只适用于各个情况(state)<可能性/概率>均等的情况?
- 直接log化概率 (MORE GENERAL) $-log_2^{p}$
- 仔细思考会知道,$\text{num of yes/no questions}=\log_{2}(\text{情况数目})=\log_{2}(1/p)$
- 不过当非等概率(且底数非2的指数倍)以及概率倒数非整数的情况下,该定义仍适用的理由还要思考清楚
- N种情况(state) -> log计算 -> 得到信息量 $\log_{2}^{N}$
- 从log计算来看, 对于概率越大的事件, 其对应信息bit越低; state越少对应信息bit也越低。反之越大。意味着越确定的事情bit越低(信息量越少),反之越大。
- Measure the average amount of information
- 相当于数学期望 (average number of yes/no questions we need to ask to get the correct answer, 参见video2, 二叉树的应用)
- $-\sum_{i}p_{i}log_{2}(p_{i})$
- That’s it, the formula calculates the entropy, which measures the uncertainty.
- $H(\text{p}) = -\sum_{i}p_{i}log_{2}(p_{i})$
- p为概率分布
- it tells how unpredictable the probability distribution is.
- 且在这里的信息都是有意义信息,无意义或冗余信息可以看作是为传递有意义信息而产生的成本,传递的信息的集合称为消息(message)
| Index | Weather | Possibility | Code | Information | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 🌞 | 0.125 | 000 | 3 bits | 3 bits |
| 1 | ⛅ | 0.125 | 001 | 3 bits | 3 bits |
| 2 | ☁ | 0.125 | 010 | 3 bits | 3 bits |
| 3 | 🌨 | 0.125 | 011 | 3 bits | 3 bits |
| 4 | 🌧 | 0.125 | 100 | 3 bits | 3 bits |
| 5 | 🌩 | 0.125 | 101 | 3 bits | 3 bits |
| 6 | 🌪 | 0.125 | 110 | 3 bits | 3 bits |
| 7 | 🌫 | 0.125 | 111 | 3 bits | 3 bits |
表1
graph tree1 {
edge [color="0.700 0.200 1.000"];
node [style=filled, color="0.650 0.200 1.000"];
overlap=false;
ABCD--AB[label="1/2"];
ABCD--CD[label="1/2"];
AB--A[label="1/4"];
AB--B[label="1/4"];
CD--C[label="1/4"];
CD--D[label="1/4"];
}
图1 (等概率,层层二分)
graph tree2 {
edge [color="0.700 0.200 1.000"];
node [style=filled, color="0.650 0.200 1.000"];
ABCD--A[label="1/2"];
ABCD--BCD[label="1/2"];
BCD--D[label="1/4"];
BCD--BC[label="1/4"];
BC--B[label="1/8"];
BC--C[label="1/8"];
}
图2 (非等概率,但可层层二分)
graph tree3 {
edge [color="0.700 0.200 1.000"];
node [style=filled, color="0.650 0.200 1.000"];
A[label="3/5"];
B[label="1/5"];
C[label="1/10"];
D[label="1/10"];
}
图3 (非等概率,不可二分? 可以考虑哈夫曼树的构建与哈夫曼编码,默认前缀编码,但是意义与上二图不同)
- Cross-Entropy
- 可以理解为传递消息(message)所需的期望信息量?
- 表2中 $\text{Entropy} = 2.23 \,\text{bits},\, \text{Cross-Entropy} = 3\,\text{bits}$
- 表3中 $\text{Cross-Entropy} = 2.42\,\text{bits}$
- $H(\text{p, q})=-\sum_{i}p_{i}\log_{2}(q_{i})$
- p为true概率分布
- q为predicted概率分布
- 提及的二表的Message列即为predicted distribution,由Code列决定
- predicted possibility加和不一定为1
- 如果预测良好(两distribution相等),则Cross-Entropy与Entropy计算数值相等; 如果predicted distribution与true distribution存在差异,则Cross-Entropy将会比Entropy大(在message进行合理编码的情况下?)
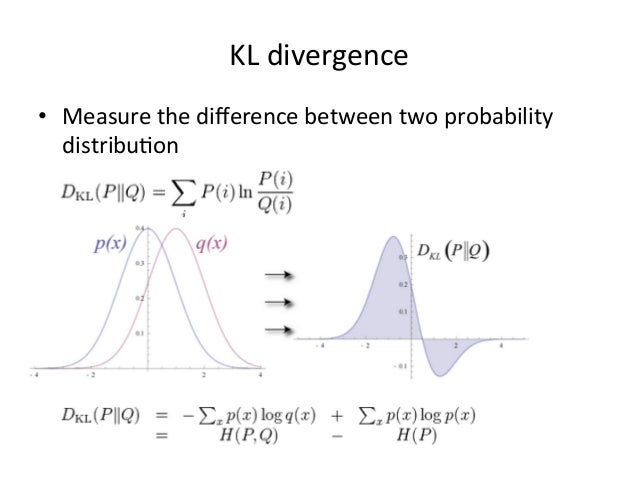
- $\text{Cross-Entropy}-\text{Entropy} \Rightarrow \text{Relative Entropy} \Rightarrow \text{Kullback-Leibler divergence}$
- $\text{Cross-Entropy} = \text{Entropy} + \text{K-L divergence}$
- K-L divergence:
- \[D_{KL}(\text{p}||\text{q})=H(\text{p, q})-H(\text{p})=-\sum_{i}p_{i}\log_{2}(q_{i})+\sum_{i}p_{i}\log_{2}(p_{i})=\sum_{i}p_{i}[log_{2}(p_{i})-log_2(q_{i})]=\sum_{i}p_{i}\log_{2}^{\cfrac{p_{i}}{q_{i}}}\]
- \[D_{KL}(P||Q)=E_{x\sim P} \left[\log \cfrac{P(x)}{Q(x)} \right]\]
- \[D(p||q)=p\log^{\cfrac{p}{q}}+(1-p)\log^{\cfrac{1-p}{1-q}}\]
- Saying: “KL divergence from q to p”
- Properties
- \[D_{KL}(P||Q)\ge 0, \forall P, Q\]
- \[D_{KL}(P||Q)=0, \text{if P and Q are equal almost surely}\]
- KL divergence is asymmetric, i.e.
- \[D_{KL}(P||Q)\ne D_{KL}(Q||P)\]
- Application: i.e. 找到一distribution Q,使得其与true distribution P最相符(且P,Q相互独立):
- \[\arg\min_{Q}D_{KL}(P||Q)\]
- 上述目的等价于$\arg\min_{Q}H(P, Q)=\arg\min_{Q}-E_{x\sim P}\left[\log Q(x)\right]$
- Cross-Entropy can act as a Cost Function: log Loss/Cross-Entropy Loss
- $H(\text{p, q})=-\sum_{i}p_{i}\log(q_{i})$
- 采用自然底数
- 换底公式: $log_2(x)=log(x)/log(2)$
| Index | Weather | Possibility | Code | Information | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 🌞 | 0.35 | 000 | 1.51 bits | 3 bits |
| 1 | ⛅ | 0.35 | 001 | 1.51 bits | 3 bits |
| 2 | ☁ | 0.1 | 010 | 3.32 bits | 3 bits |
| 3 | 🌨 | 0.1 | 011 | 3.32 bits | 3 bits |
| 4 | 🌧 | 0.04 | 100 | 4.64 bits | 3 bits |
| 5 | 🌩 | 0.04 | 101 | 4.64 bits | 3 bits |
| 6 | 🌪 | 0.01 | 110 | 6.64 bits | 3 bits |
| 7 | 🌫 | 0.01 | 111 | 6.64 bits | 3 bits |
表2
| Index | Weather | Possibility | Code | Information | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 🌞 | 0.35 | 00 | 1.51 bits | 2 bits |
| 1 | ⛅ | 0.35 | 01 | 1.51 bits | 2 bits |
| 2 | ☁ | 0.1 | 100 | 3.32 bits | 3 bits |
| 3 | 🌨 | 0.1 | 101 | 3.32 bits | 3 bits |
| 4 | 🌧 | 0.04 | 1100 | 4.64 bits | 4 bits |
| 5 | 🌩 | 0.04 | 1101 | 4.64 bits | 4 bits |
| 6 | 🌪 | 0.01 | 11100 | 6.64 bits | 5 bits |
| 7 | 🌫 | 0.01 | 11101 | 6.64 bits | 5 bits |
表3 (unambiguous code: prefix Huffman code)
| Code | Bit | Note |
|---|---|---|
| 00 | 2 | |
| 01 | 2 | |
| 100 | 3 | 前2位已被上一级占,采用进位生成新前2位 |
| 101 | 3 | |
| 1100 | 4 | 前3位已被上一级占,采用进位生成新前3位 |
| 1101 | 4 | |
| 11100 | 5 | 前4位已被上一级占,采用进位生成新前4位 |
| 11101 | 5 |
表4 (前缀编码/prefix code)
| P(red) | P(Blue) | P(winning) | -log2(P(winning)) | Entropy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 🔴🔴🔴🔴 | 1 | 0 | 1*1*1*1=1 | 0+0+0+0=1 | 0 |
| 🔴🔴🔴🔵 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.75*0.75*0.75*0.75=0.105 | 0.415+0.415+0.415+2 | 0.81 |
| 🔴🔴🔵🔵 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5*0.5*0.5*0.5=0.0625 | 1+1+1+1 | 1 |
表5
- More details about KL divergence
- Given P, we want to find Q* that minizes the KL divergence
- 由于KL divergence是不对称的,有两种最小化
- 参见图6

Reference
- 📺 Entropy, Cross-Entropy and KL-Divergence
- 📺 Shannon Entropy and Information Gain
- 📺 Khan Academy, Shannon Entropy
- 📺 KL Divergence
Application in Multi-Criteria Decision-Making
- 熵值法可以作为一种客观赋权方法
- 设有m个待评方案(样本Sample),n项评价指标(特征Feature),形成元素指标数据矩阵$X=(x_{ij})_{m\times n}$
- 根据熵的特性,可以通过计算熵值来判断一个方案的随机性及无序程度,也可以用熵值来判断某指标的离散程度,指标的离散程度越大,该指标对于综合评价的影响越大
- Data Preprocessing
- 量纲不影响,无需标准化
- 数据非负化处理
- 数据平移 (2种平移方式,前者处理越大越好的数据,后者处理越小越好的数据,最终都是越大越好)
- $x_{ij}=\cfrac{x_{ij}-\min(x_{1j},…,x_{mj})}{\max(x_{1j},…,x_{mj})-\min(x_{1j},…,x_{mj})}+1$
- $x_{ij}=\cfrac{\max(x_{1j},…,x_{mj})-x_{ij}}{\max(x_{1j},…,x_{mj})-\min(x_{1j},…,x_{mj})}+1$
- 算法思路: 计算出每列的Entropy, Entropy越小的权重越大
- 其中possibility: $p_{ij}=\cfrac{x_{ij}}{\sum_{i}^{m}x_{ij}}$
- entropy: $e_{j}=-\sum_{i}^{m}p_{ij}\ln(p_{ij}) \rightarrow e_{j}=\cfrac{e_{j}}{\ln{m}} \Leftrightarrow e_{j}=-\cfrac{1}{\ln{m}}\sum_{i}^{m}p_{ij}\ln(p_{ij})$
- 多一个系数$1/\ln{m}$代表着m种情况都均等概率(默认概率和必为1)时的entropy值,此时的entropy最大(离散程度最低),此系数保证计算出的值在0-1内
- 差异系数: $g_{j}=1-e_{j}$
- weight: $w_{j}=\cfrac{g_{j}}{\sum_{j}^{n}g_{j}}$
- score: $s_{i}=\sum_{j}^{n}w_{j}*p_{ij}$